Health
Proposed GMO Mosquitoes: Africans Advised To Be Wary Of WHO
By Chinasa Obidi
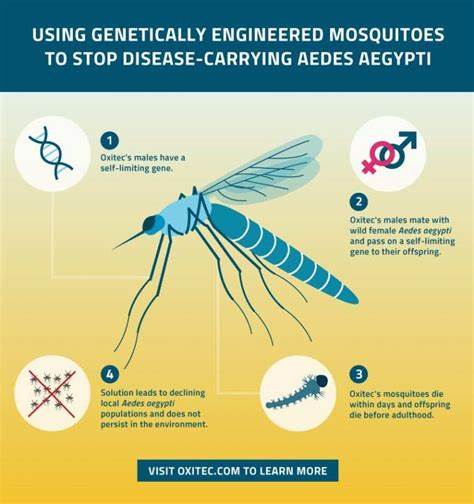
Kenyan Dr Wahome Ngare, the founding Director of Mercy Health Services, Nairobi, Kenya, has advised Africans to be wary of the World Health Organisation, WHO’s proposed introduction of GMO mosquitoes into Africa to eradicate malaria, as well as the malaria vaccine which he says will be made compulsory.”
But malaria is a treatable disease which we have been using our herbal teas to treat, plus we are unaware of the risks such GMO mosquitoes would bring,” he said, calling on Africans to exercise caution in this regard.
He said that while the WHO has done a lot of good things for the continent, it has equally done things that have affected Africa and Africans negatively making him advice African countries to exercise caution.He expressed this warning while addressing Ugandan President, Yoweri Kaguta Museveni in a trending video.
He gave his reasons for sounding the warning this: “In 2014/2015, WHO brought tetanus eradication campaign in our country; a campaign to eradicate neonatal tetanus.
“The vaccine that was used is a different type of tetanus vaccine that is fertility regulating, where they take tetanus and a hormone called Human Chorionic Conadotropin, and when you inject a woman with that vaccine, she produces antibodies against that hormone and is therefore rendered sterile.
“So we are now seeing an increase in infertility cases amongst young couples who are certified okay when examined, but cannot get children, or couples who are losing three to five pregnancies before they are able to cary any pregnancy to term.
“We were able to expose this through a paper we published, and fortunately in 2017, WHO said Kenya is now free of neonatal tetanus and they left our country.”But they developed this vaccine in an over twenty year period of research from 1972 to 1992 and used that vaccine in South America and possibly many other African countries.
“Responding to this call, Benjamin Amodu, a professor of Phytho-medicine from the Triune Biblical University, USA, who has been at the forefront of advocating for the use of herbal medicine, said Nigerians and Indeed Africans should also evaluate and verify any treatment or vaccine that is given to them before going ahead to use them.
“I think this is a very common view all around . I think we can cooperate with the WHO in most of the things and we can also evaluate to see that is in line with our own aspiration as a country just like the Ugandan and Kenyan doctors did to their president.
“It is a welcome development. We should ensure that whatever is being brought upon us should be well evaluated to see and if there are needs for modification, they should be modified to the interest of who they are introducing the the programme to.
” Even their comment on malaria, I think the WHO should be more open. Irrespective of where whatever treatment or vaccine is coming from, so long as it meets the requirements should be accepted and adopted so we move forward.
“I therefore call on African leaders and people to exercise faith in our God given natural herbs , carry out extensive research and promote it because even diseases for which the cures have eluded modern medicine for decades are being effectively cured with the use of Traditional, Complimentary and Herbal Medicines, TCAM, without any side effects.”
It would be recalled that Prof Amodu’s malaria cure was evaluated by the United Nations and found to be more effective than chloroquine and palaudrine.
Health
APC Youth Leader, Health Minister, Others Champion “Going Pink Walk” for Breast Cancer Awareness in Abuja


Joel Ajayi
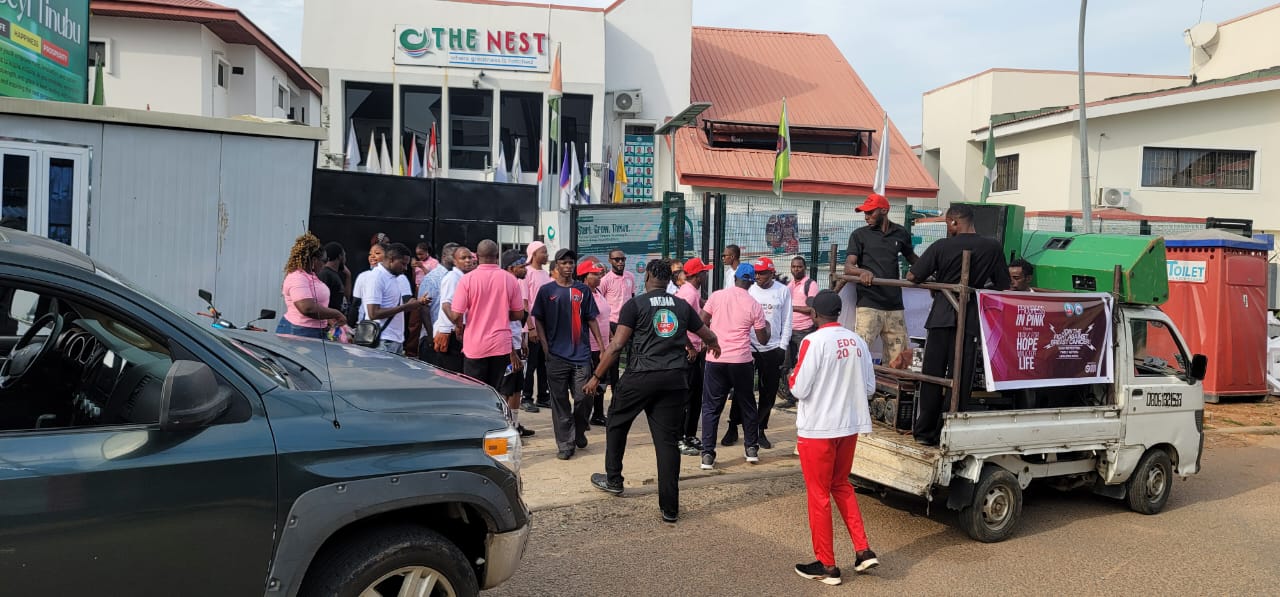
It was a vibrant gathering of energetic young men and women across the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) on Saturday in Abuja, as they joined the “Progress in Pink Walk”, a non-competitive awareness march organized by the All-Progressives Congress (APC) Youth Wing to mark Breast Cancer Awareness Month.
The event, themed “Walk for Hope, Walk for Life,” was commenced at The Nest — A Place Where Greatness is Hatched, an over 4 kilometres walk aimed at encouraging early detection, promoting timely medical intervention, and offering hope to those affected by breast cancer.
Leading the walk was the APC National Youth Leader, Dr. Dayo Israel, who has remained consistent in championing initiatives that promote youth empowerment, health consciousness, and community impact.
Over the years, Israel has spearheaded several programs designed to enhance the capacity and wellbeing of young Nigerians.
Globally, October is recognized as Breast Cancer Awareness Month — a period dedicated to increasing awareness, encouraging prevention, and supporting those battling the disease. The APC Youth Wing’s initiative aligns with this global campaign, demonstrating the party’s ongoing commitment to public health advocacy and youth-driven change.
Speaking after the walk, an elated Dr. Dayo Israel explained that the initiative was organized to create awareness among women, both young and old, on the importance of knowing their bodies and seeking medical attention early.
“We want women to know their breasts so well that if anything unusual happens, they act quickly.
“Cancer doesn’t occur overnight it develops over time. awareness, and early detection are key to saving lives,” he said.
He added that the walk also sought to promote fitness as a vital component of a healthy lifestyle and to encourage women to adopt positive habits that support their wellbeing and happiness.
In his remarks, the Minister of State for Health and Social Welfare, Dr. Iziaq Adekunle Salako commended the APC Youth Wing for taking proactive steps to raise awareness about a critical health concern.
“With this step you have taken today, more Nigerians will become aware of the dangers of late detection.
“Unfortunately, eight to nine out of ten breast cancer cases in Nigeria are detected late — a situation we must change through constant awareness and screening,” he said.
He emphasized the importance of prevention, urging Nigerians to take their health seriously through regular check-ups, healthy living, and avoidance of risk factors like smoking.
Also speaking, the President and CEO of the Nigerian Cancer Society, Prof. Abidemi Omonisi, noted that breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent forms of cancer in Nigeria, accounting for up to 40–50% of all cancer cases.
“Breast cancer remains a major public health challenge. Exercise plays a vital role not only in prevention but also in improving outcomes for people living with cancer and other non-communicable diseases such as diabetes and hypertension,” he said.
Prof. Omonisi stressed the need for a community-based response to cancer similar to the national efforts used to combat HIV/AIDS.
“We must involve everyone from schools and youth groups to community organizations to build resilience and eliminate the fear and stigma surrounding cancer,” he added.
He praised the APC Youth Wing for leading the charge, noting that young people, with their creativity and innovation, are uniquely positioned to drive impactful awareness campaigns both online and offline.
The “Progress in Pink Walk” concluded with participants pledging to continue spreading the message of early detection, regular screening, and healthy living underscoring that together, Nigerians can defeat breast cancer through awareness, unity, and action.
-

 Featured6 years ago
Featured6 years agoLampard Names New Chelsea Manager
-

 Featured6 years ago
Featured6 years agoFG To Extends Lockdown In FCT, Lagos Ogun states For 7days
-

 Featured6 years ago
Featured6 years agoChildren Custody: Court Adjourns Mike Ezuruonye, Wife’s Case To April 7
-

 Featured6 years ago
Featured6 years agoNYSC Dismisses Report Of DG’s Plan To Islamize Benue Orientation Camp
-

 Featured4 years ago
Featured4 years agoTransfer Saga: How Mikel Obi Refused to compensate me After I Linked Him Worth $4m Deal In Kuwait SC – Okafor
-
Sports3 years ago
TINUBU LAMBAST DELE MOMODU
-

 News10 months ago
News10 months agoZulu to Super Eagles B team, President Tinubu is happy with you
-
Featured6 years ago
Board urges FG to establish one-stop rehabilitation centres in 6 geopolitical zones
